The colloquium offers survey talks in mathematics and related fields, the time for all the faculty and graduate students to get together to learn of somebody else's perspective on mathematics, and to broaden their own. A colloquium talk should be addressed to a general mathematical audience rather than technical details for specialists. The first 15 minutes should be completely understandable to graduate students.
The colloquium talks begin on Tuesdays at 2:00 p.m. Colloquium coffee succeeding talks around 3:00 pm.
Contact: Jiange LI (jiange.li AT hit.edu.cn)
Upcoming talks
Past talks
January22 2026. 10:00(Beijing time)
Speaker:Jinyuan Chang (Southwestern University of Finance and Economics)
Title:CP-factorization for high dimensional tensor time series and double projection iterations
Abstract
We adopt the canonical polyadic (CP) decomposition to model high-dimensional tensor time series. Our primary goal is to identify and estimate the factor loadings in the CP decomposition. We propose a one-pass estimation procedure through standard eigen-analysis for a matrix constructed based on the serial dependence structure of the data. The asymptotic properties of the proposed estimator are established under a general setting as long as the factor loading vectors are algebraically linear independent, allowing the factors to be correlated and the factor loading vectors to be not nearly orthogonal. The procedure adapts to the sparsity of the factor loading vectors, accommodates weak factors, and demonstrates strong performance across a wide range of scenarios. A tractable limiting representation of the estimator is derived, which plays a key role in the related inference problems. To further reduce estimation errors, we also introduce an iterative algorithm based on a novel double projection approach. We theoretically justify the improved convergence rate of the iterative estimator, and also provide the associated limiting distribution. All results are validated through extensive simulations and a real data application.
January13 2026. 11:30(Beijing time)
Speaker:袁新意 (北京大学)
Title:Equidistribution over finitely generated fields
Abstract
The goal of this talk is to present some conjectures, examples, and theorems about equidistribution of small points over finitely generated fields. The main results are joint work with 郭若一、商来、杨诚远。
January13 2026. 09:45(Beijing time)
Speaker:谢俊逸(北京大学)
Title:Rational points on loxodromic K3 surfaces
Abstract
This talk is based on the work with Damian Gvirtz-Chen, Zhizhong Huang and Zhuchao Ji. We establish the potential Hilbert property for all K3 surfaces over number fields which admit an automorphism of positive entropy. Our method draws ingredients from both algebraic geometry and holomorphic dynamics.
January9 2026. 08:30(Beijing time)
Speaker:王凤雨(天津大学)
Title:Nonlinear functional inequalities for ergodicity rate of generalized porous media equations
Abstract
We introduce several nonlinear functional inequality to characterize different type convergence rates of generalized porous media equations, and present criteria to verify these inequalities. Some concrete examples are presented to verify the main results. The talk is based on an ongoing joint work with Xing Huang and Michael Rockner.
January9 2026. 09:10(Beijing time)
Speaker:张土生(中国科学技术大学)
Title:Exponential ergodicity of stochastic evolution equations with reflection
Abstract
In this paper, we establish an exponential ergodicity for stochastic evolution equations with reflection in an infinite dimensional ball. As an application, we obtain the exponential ergodicity of stochastic Navier-Stokes equations with reflection. A coupling method plays an important role.
January9 2026. 10:10(Beijing time)
Speaker:郭先平(中山大学)
Title:Nonstationary zero-sum Markov games with the probability criterion
Abstract
This paper studies a two-person non-stationary stochastic game under a probability criterion, which focuses on the probability that the accumulated rewards of player 1 (i.e., the costs of player 2) exceed a prescribed threshold before the first passage into a target set. We first present two illustrative examples. The first one shows that the probability criterion breaks the implication from a nonzero-sum Nash equilibrium to a zero-sum saddle point. The second demonstrates that the non-stationary game can not be transformed into an equivalent and stationary one via the standard state augmentation. Because of the non-stationariness, we introduce the notion of the n-th value of game from time n onwards. Under a mild condition, we prove that the sequence of the n-th values is the unique solution of the system of Shapley equations for the probability criterion. From the system of Shapley equations, we establish the existence of the value and a saddle-point for the game, give an iteration algorithm for computing the approximation value and ϵ-saddle-points of the game, and provide convergence guarantees together with explicit error bounds. Finally, an energy management numerical example is presented to illustrate the theoretical results and the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm.
January9 2026. 10:50(Beijing time)
Speaker:宋仁明(伊利诺伊大学厄巴纳-香槟分校)
Title:Heat kernel estimates for Markov processes with jump kernels blowing-up at the boundary
Abstract
In this talk, I will present some recent results about purely discontinuous symmetric Markov processes on closed subsets of Rd , d ≥ 1, with jump kernels of the form J(x, y) = |x − y|-d-α B(x, y), α ∈ (0, 2), where the function B(x, y) may blow up at the boundary of the state space.
Examples of Markov processes that fall into our general framework include traces of isotropic α-stable processes in C1,Dini sets, processes in Lipschitz sets arising in connection with the nonlocal Neumann problem, and a large class of resurrected self-similar processes in the closed upper half-space.
Our main results are sharp two-sided heat kernel estimates for these Markov processes. A fundamental difficulty in accomplishing this task is that, in contrast to the existing literature on heat kernels for jump processes, the tails of the associated jump measures in our setting are not uniformly bounded.
Thus, standard techniques in the existing literature used to study heat kernels are not applicable.To overcome this obstacle, we employ recently developed weighted functional inequalities specifically designed for jump kernels blowing up at the boundary. This talk is based on a joint paper with Soobin Cho, Panki Kim and Zoran Vondracek.
December12 2025. 10:00(Beijing time)
Speaker:金龙(清华大学)
Title:Counting Pollicott-Ruelle resonances for Axiom A flow
Abstract
In 1980's, Pollicott and Ruelle independently introduced the concept of resonances for hyperbolic dynamical systems, for example, Smale's Axiom A flows. They are the poles of the meromorphic continuation of the Laplace transform of the correlation function and thus connected to the mixing property of the system. They are also closely related to the zeros and poles of the dynamical zeta function which is connected to the distribution of periods for closed orbits in the system. In the special cases of Anosov flows, their distributions have been well studied since the work of Faure-Sjostrand in 2010. In this talk, we present the first counting result on Pollicott-Ruelle resonances for general Axiom A flows satisfying strong transversal condition. In particular, we give a polynomial upper bound and a sublinear lower bound on the number of resonances in strips. This is based on joint work with Tao Zhongkai.
September2 2025. 10:00(Beijing time)
Speaker:李洪全(复旦大学)
Title:二步Carnot群上距离初探
Abstract
本报告希望通过一些最简单的例子来说明:在二步群的框架下,我们如何利用热核这一分析工具来研究任意两点之间距离,后者是几何中的一个基本问题。
August31 2025. 15:00(Beijing time)
Speaker:张益唐(中山大学香港高等研究院)
Title:The Landau-Siegel Zero Problem: History and Recent Progress
Abstract
The Landau-Siegel zero problem is a special and important case of the Generalized Riemann Hypothesis. It was first introduced by Dirichlet in 1837 when he proved his celebrating result on the prime numbers in arithmetic progressions. Since then, many experts of number theory were attracted by this problem. In this talk, I will cover the history, application and recent progress on this famous problem.
August12, 2025. 15:00(Beijing time)
Speaker:席南华(中国科学院)
Title:几何 -- 从熟悉到陌生
Abstract
我们将从几何的发展过程中看几何是怎样从欧式几何演变到让人眼花缭乱的几何世界。
August11, 2025. 16:00(Beijing time)
Speaker:叶向东(中国科学技术大学)
Title:Recurrence in dynamics and applications
Abstract
Recurrence is one of the most important properties in dynamical systems. It turns out that recurrence also has many profound applications in combinatorial number theory. In this talk I will review some known results concerning recurrence and the applications. In the process I will also explain the main tools used and under development, and state some recent results and some open questions.
August11, 2025. 14:30(Beijing time)
Speaker:张继平(北京大学)
Title:数字的力量
Abstract
人类的文明史,启始于文字的发明,人类最早出现的文字实际上是表示数的文字-- 数字, 因此数字的形成是人类文明发展的起始点和源泉。今天,电子信息的所有机器语言都是用数字代表的,我们正处于数字时代,也就是数字技术的时代,数字技术本质上是数学技术。数字的力量体现的是数学的力量。
August2, 2025. 15:00(Beijing time)
Speaker:田野(中科院)
Title: L-函数和算术
Abstract
L函数包括欧拉-黎曼zeta函数,椭圆曲线的L函数等。我们介绍L函数的历史和发展,以及它们和算术问题的联系。
August1, 2025. 15:30(Beijing time)
Speaker:袁亚湘(中科院)
Title:计算---第三种科学方法
Abstract
长期以来,实验和理论是两大科学研究的方法。随着现代计算机的出现和迅猛发展,计算已经成为第三种科学方法。本报告简要介绍计算的历史、现状和发展趋势。报告将综述计算工具的进化以及计算方法的发展,将对有史以来的若干重要计算方法其及思想给予介绍。
July21, 2025. 16:30(Beijing time)
Speaker:Gilles Pisier (法国巴黎六大,美国德州农工大学)
Title:Lifting properties for C* -algebras
July21, 2025. 11:00(Beijing time)
Speaker:范爱华(法国Picardie大学,武汉大学)
Title:遍历定理(Ergodic Theorems)
Abstract
遍历定理源自统计物理,它揭示了自然界的某种普遍现象,它遍布于大多数极限行为当中,一百多年来备受瞩目。我们将介绍最经典的遍历理论,也将介绍遍历定理的新形式,如遍历级数、加权遍历定理、遍历Hilbert变换等。同时,我们也将涉及遍历理论在数论与科学计算中的应用。
June24, 2025. 14:30(Beijing time)
Speaker:文志英(清华大学)
Title:数学学习中的训练和思考
Abstract
通过学习过程中一些熟知的例子做一些逐步深入的讨论,涉及到对一些基本概念、思想和方法的深入理解,特别是增强对数学的感觉和认识。
June6, 2025. 15:30(Beijing time)
Speaker:吉国兴(陕西师范大学)
Title:Interpolation problems in subdiagonal algebras
Abstract
In this talk, we will discuss interpolation problems in subdiagonal algebras. Let A be a subdiagonal algebra in a ![]() -finite von Neumann algebra M. We mainly consider the interpolation problem in A with the universal factorization property. We determine when a finitely generated left ideal in A is trivial. By constructing a periodic flow on M according to a type 1 subdiagonal algebra, we show that type 1 subdiagonal algebras coincide with analytic operator algebras associated with periodic flows in von Neumann algebras. This enables us to present a form decomposition of a type 1 subdiagonal algebra. As an application, we deduce a noncommutative operator-theoretic variant of the Corona theorem for type 1 subdiagonal algebras.
-finite von Neumann algebra M. We mainly consider the interpolation problem in A with the universal factorization property. We determine when a finitely generated left ideal in A is trivial. By constructing a periodic flow on M according to a type 1 subdiagonal algebra, we show that type 1 subdiagonal algebras coincide with analytic operator algebras associated with periodic flows in von Neumann algebras. This enables us to present a form decomposition of a type 1 subdiagonal algebra. As an application, we deduce a noncommutative operator-theoretic variant of the Corona theorem for type 1 subdiagonal algebras.
May27, 2025. 10:00(Beijing time)
Speaker:王清(厦门大学)
Title:Parafermion vertex operator algebras: from coset to orbifold
Abstract
Coset construction and orbifold construction are two important ways to construct new vertex operator algebras (VOAs) from given ones. Parafermion VOA is a special kind of coset construction related to the affine VOA. In this talk, I will present our recent results on the structures and representations of affine VOAs, Parafermion VOAs and their orbifolds.
May22, 2025. 14:00(Beijing time)
Speaker:朱蓉禅(北京理工大学)
Title:$\Phi^4_3$ Theory from many-body quantum Gibbs states
Abstract
We derive the $\Phi^4_3$ measure on the torus as a rigorous limit of the quantum Gibbs state of an interacting Bose gas, where the limiting classical measure describes the critical behavior of the Bose gas just above the Bose--Einstein phase transition. Since the quantum problem is typically formulated using a nonlocal interaction potential, a key challenge is to approximate the local $\Phi^4_3$ theory by a Hartree measure with a nonlocal interaction. This requires uniform estimates on the Hartree measure, which are achieved using techniques from recent development on stochastic quantization and paracontrolled calculus. The connection to the quantum problem is then established by applying the variational approach and deriving a quantitative convergence of the quantum correlation functions to those of the Hartree classical field.
April18, 2025. 14:00(Beijing time)
Speaker:喻良(南京大学)
Title:算法随机性理论简介
Abstract
我们简要介绍算法随机性理论及其应用。算法随机性理论起源于Kolmogorov, Solomonoff, Chaitin等人,主要是关于随机性概念的基础理论研究。二十世纪末递归论进入到算法随机性理论中,使得这一理论获得了快速的发展。我们将简要介绍这些成果及其应用。
April10, 2025. 10:00(Beijing time)
Speaker:郭少明(南开大学)
Title: 分形集的正交投影定理
Abstract
报告的内容是关于分形集的正交投影定理,以及它们与调和分析中的极大算子的联系。
March31, 2025. 15:00(Beijing time)
Speaker:Sergey Kitaev(University of Strathclyde)
Title: What is a good bijection? A case study on pattern-avoiding permutations
Abstract
A bijection is a one-to-one correspondence between two sets. Usually, there is more than one way to build a bijection between equinumerous sets (and there are of course many if the sets aren't very small and we don't care whether the bijections are intelligible). What is a good bijection between two sets? Is it one that is easy to describe? Or, is it one that better illuminates structural similarity between the sets in question? Even though the answer “it depends” is acceptable here, much more can be said under certain assumptions in certain situations. I will illustrate this idea by going through a remarkable story of a problem in the theory of permutation patterns.
January8, 2025. 09:50(Beijing time)
Speaker:李向东(中国科学院数学与系统科学研究院)
Title: On the Navier-Stokes and Euler equations via the Bellmann programming dynamical principle on G=SDiff(M)
Abstract
In 1966, V.I. Arnold proved that the Euler equation of the ideal fluid over a Riemannian manifold M can be regarded as the geodesic on the group of volume preserving diffeomorphsims G=SDiff(M). Since then, many people have extended Arnold's idea to the incompressible Navier-Stokes equation. In this talk, I will present some recent results on the study of the Navier-Stokes and Euler equations via the Bellmann programming dynamical principle on G=SDiff(M). Joint work with Guoping Liu (HUST, Wuhan).
January8, 2025. 08:10(Beijing time)
Speaker:巩馥洲(中国科学院数学与系统科学研究院)
Title: 基于重整化群的深度神经网络可解释性研究
Abstract
将深度神经网络的输入数据集看成一个统计物理系统,并将其输出的重要特征量看成输入数据集这一统计物理系统的宏观特征。基于统计物理中的重整化群理论,将深度神经网络的随机梯度下降算法等求解算法视为一种粗粒化型重整化过程,证明了它与输入数据集的典则重整化过程的等效性。由此知,深度神经网络有能力提取到输入数据集的宏观特征,从理论上给出了深度神经网络的可解释性。本报告将首先简单介绍重整化群理论的基本思想及所研究的深度神经网络,其次将分别介绍关于一维伊辛模型和一类指数族分布函数描述的输入数据集的研究结果,最后将介绍未来进一步的研究。
January7, 2025. 09:50(Beijing time)
Speaker:董昭(中国科学院数学与系统科学研究院)
Title: Some recent progress on stochastic 3D Burgers equation
Abstract
This report introduces some recent research progress on the well-posedness and ergodicity of 3D stochastic Burgers equation, which was completed in collaboration with Professor Zdzislaw Brzezniak, Jianglun Wu, Guoli Zhou , and Shijia Zhang.
January3, 2025. 14:30(Beijing time)
Speaker:Caucher Birkar (Tsinghua University)
Title: Geometry and Integers
Abstract
In this talk we will discuss some recent interesting connections between properties of sets of non-negative integers with different kinds of geometries. Starting with a primitive integer vector, we examine certain associated functions and relate the setting to statements in convex, toric, and birational geometries.
December29, 2024. 09:00(Beijing time)
Speaker:李嘉禹(中国科学技术大学)
Title: PDE methods in geometric analysis
Abstract
In the talk we will review PDE methods in geometric analysis, mainly Li-Yau gradient estimates, Sacks-Uhlenbeck blow-up analysis, and the geometric flow method. We will also talk our results in the fields.
December28, 2024. 17:25(Beijing time)
Speaker:李松(浙江大学)
Title: 压缩感知及其相关领域中的几个基本核心问题
Abstract
小波分析、压缩感知、低秩矩阵恢复以及相位恢复理论构成了数据科学的重要数学基础,演讲内容首先将从小波分析的视角探讨压缩感知领域的发展历程,之后将介绍压缩感知、低秩矩阵恢复以及相位恢复领域中的一些基本核心问题,例如:这些领域中几个著名的恢复理论与求解算法问题(包括:压缩感知奠基人之一、ICM 1小时报告人E. Candes、国际杰出统计学家,统计学最高奖“考普斯总统奖”得主蔡天文等所提出的几个公开问题与猜想等)。针对于这些公开问题与猜想,我们给予了正面回答。这些工作是我与合作者一起近十年以来所取得的研究成果。
December28, 2024. 09:00(Beijing time)
Speaker:章志飞(北京大学)
Title: Blow-up for the supercritical defocusing nonlinear wave equation
Abstract
In this talk, we introduce our recent result on the finite time blow-up for the supercritical defocusing nonlinear wave equation (NLW) in ![]()
The proof of this result is based on a surprising connection between complex-valued NLW and relativistic Euler equations, and the construction of self-similar imploding solutions of the relativistic Euler equations.
December24, 2024. 14:00(Beijing time)
Speaker:Su Gao(Nankai University)
Title: 数学中分类问题的复杂度
Abstract
在众多数学分支中,数学对象的分类问题往往具有核心的地位。直观上,有些分类问题比较简单,有些则非常复杂。在这个报告中我们通过一些实例来介绍一个可以严格探讨数学中分类问题的相对复杂性的数学理论,即等价关系的描述集合论。我们将展示如何将这一理论应用到数学分类问题的研究中去。
December20, 2024. 14:00(Beijing time)
Speaker:Su Gao(Nankai University)
Title: The Herwig-Lascar Property of Groups
Abstract
Herwig and Lascar, in their celebrated paper of 1992, proved the EPPA for some general classes of structures by showing that finitely generated free groups have certain combinatorial property. We call this property the Herwig-Lascar property (HL-property for short) and explore further results. For instance, we show that the HL-property is closed under free products. We also establish explicit equivalences between the HL-property of groups and extensions of structures on which the group acts. As an application, we prove that the automorphism group of any Henson graph contains a dense locally finite subgroup that is isomorphic to Hall's group. This is joint work with Mahmood Etedadialiabadi, François Le Maître, and Julien Melleray.
December19, 2024. 14:00(Beijing time)
Speaker:向开南(湘潭大学)
Title: 是否每个可数无穷图都有一个不友好剖分?
Abstract
猜想:每个可数无穷图都有一个不友好顶点二剖分,即此二剖分使每个顶点在自己所属的类里的邻居数不超过在另一个类里的邻居数。
这是无穷图论中有35年历史的最著名猜想之一,见R. Diestel [2016. Graph theory (5th edition). Springer.]第8.1节。它易于陈述,能被稍有数学基础的人理解,但又极具挑战性。从Open Problem Garden (http://www.openproblemgarden.org/)可以得知,它的重要性为3星;概率论中的 KPZ Universality Conjecture、数论中的The 3n+1 Conjecture (The 3x+1 Problem)的重要性也是3星;此处重要性的最高等级为4星,黎曼猜想是4星。
“20世纪数学的一个了不起的发展是认识到有时候可以用概率方法来证明一些看起来并没有概率本性的数学命题。” 见N. Alon(Wolf数学奖得主)和M. Krivelevich(2008. Extremal and probabilistic combinatorics, in The Princeton Companion to Mathematics)。
此未决猜想能否被概率方法攻克?我们的答案是肯定的。此报告基于多年的探索[Xiang Kainan, (2019-2024), Every countable infinite graph admits an unfriendly partition, Preprint.], 其中位置渗流、概率测度的弱收敛理论及一个新颖的拓扑与度量构造起着关键的作用。
December4, 2024. 14:00(Beijing time)
Speaker:Lijian Yang(Tsinghua University)
Title: Extreme distribution of Gaussian processes and its role in statistical inference
Abstract
Distributions of Gaussian process extremes (supremum, infimum and absolute supremum) is a subject long studied in probability theory, yet its relevance to statistical inference is inadequately understood. I will illustrate with examples of simultaneous confidence regions (SCRs), and present some recent results on exact quantiles of Gaussian process extremes which provide the indispensable theoretical underpinning of the SCR methodology.
August16, 2024. 09:30(Beijing time)
Speaker:Gabrielle Demange(巴黎经济学院)
Title: Resolutions in a system of financially linked firms: Bankruptcy, defaults, and proportionality
Abstract
In a financial system, firms hold debts both within and outside the system. The reimbursement abilities are intertwined, thereby potentially generating coordination failures and a cascade of defaults. To avoid such failures and account for the links in the system, an orderly resolution liquidates all debts simultaneously and assigns the amount each firm receives and reimburses both inside and outside the system. I present properties that determine which firms are left bankrupt and how much the non-bankrupt ones reimburse and receive. The main properties are the priority of external creditors at the system level and the proportionality principle.
August13, 2024. 14:00(Beijing time)
Speaker:孙业能(新加坡国立大学)
Title: Continuous-time random matching: A general model
Abstract
We develop a general model for independent random matching of a large population in a continuous time dynamical system. We work with a general (and possibly infinite) type space for the agents and construct a continuum of independent continuous-time Markov processes that is derived from random mutation, random matching with enduring partnership, random type changing and random break up. lt follows from the exact law of large numbers that the deterministic evolution of the agents' realized type distribution for such a continuous-time dynamical system can be determined by a system of measure-valued differential equations. The results provide the first mathematical foundation for a large literature on continuous-time search-based models of labor markets, money, and over-the-counter markets for financial products.
August7, 2024. 09:00(Beijing time)
Speaker:巩馥洲(中科院)
Title: Scaling exponents for 2D percolation via Liouville quantum gravity
Abstract
In this talk we extend the fundamental gap comparison theorem of Andrews and Clutterbuck to the infinite dimensional setting. More precisely, we proved that the fundamental gap of the Schrödinger operator ![]() (
( ![]() is Ornstein-Uhlenbeck operator) on the abstract Wiener space is greater than that of the one dimensional operator
is Ornstein-Uhlenbeck operator) on the abstract Wiener space is greater than that of the one dimensional operator ![]() , provided that
, provided that ![]() is a modulus of convexity for
is a modulus of convexity for ![]() . Similar result is established for the diffusion operator
. Similar result is established for the diffusion operator ![]() Furthermore, we give the probabilistic proofs of fundamental gap conjecture and spectral gap comparison theorem of Andrews and Clutterbuck in finite dimensional case via the coupling by reflection of the diffusion processes.
Furthermore, we give the probabilistic proofs of fundamental gap conjecture and spectral gap comparison theorem of Andrews and Clutterbuck in finite dimensional case via the coupling by reflection of the diffusion processes.
August3, 2024. 10:30(Beijing time)
Speaker:孙鑫(北京大学)
Title: Scaling exponents for 2D percolation via Liouville quantum gravity
Abstract
I will first review the recent derivation of the backbone exponent for 2D percolation via Liouville quantum gravity, based on the joint work with Nolin, Qian, and Zhuang. Then I will present a few further results obtained in this fashion, based on joint works with Ang, Liu, Xu, Yu, Zhang. It remains a challenge to understand these results using a more direct method without quantum gravity.
July17, 2024. 16:30(Beijing time)
Speaker:梅韬(Baylor University)
Title: An extension of Hilbert transform to hyperbolic groups
Abstract
The classical Hilbert transform has a natural analogue on the nonabelian free groups by decomposing the free group into disjoint subsets according to the first letter of the reduced words. Mei and Ricard prove that such a transform (decomposition) is unconditional with respect to the noncommutative Lp norm associated with the free group von Neumann algebras for all 1<p<\infty. I plan to talk about a possible extension of the Lp unconditionality of such “transforms” to the general hyperbolic groups.
July12, 2024. 11:00(Beijing time)
Speaker:雷震(复旦大学)
Title: Energy Casecade for Hamiltonian Nonlinear Klein-Gordon Equations
Abstract
In this talk we consider nonlinear Klein-Gordon equations with potential. We prove that spatially localized and time-periodic bound states of the linear problem may be destroyed by generic nonlinear Hamiltonian perturbations, via energy transfers from the discrete to continuum modes and slow radiation of energy to infinity. We explore the underlying mechanism (generalized Fermi's Golden Rule) of such phenomenon and give descriptions on the transfer rate in the full generality: small or large and single or multiple eigenvalues, high dimensional eigenspaces. This settles a long-standing problem raised in the paper of Soffer-Weinstein 1999, in which single and large eigenvalue case was first treated. This is a jiont work with my students Jie Liu and Zhaojie Yang.
July7, 2024. 15:00(Beijing time)
Speaker:王凤雨(天津大学)
Title: Spectral Representations on Wasserstein Limits of Empirical Measures on Manifolds
Abstract
Sharp convergence rates in Wasserstein distance are derived for empirical measures of diffusion processes on Riemannian manifolds, and the renormalization limits are explicitly formulated by using eigenvalues and eigenfunctions of the associated elliptic operator. For explosive diffusion processes, the convergence is described by conditional expectations.
July6, 2024. 14:30(Beijing time)
Speaker:Tuomas Hytönen(Aalto University)
Title: Singular integrals in uniformly convex spaces
Abstract
We consider the action of finitely truncated singular integral operators on functions taking values in a Banach space. Such operators are bounded for any Banach space, but we show a quantitative improvement over the trivial bound in any space renormalizable with uniformly convex norm, which is equivalent to probabilistic estimates known as martingale type and cotype. The proof, which is based on the representation of a singular integral as an average of dyadic model operators over a random choice of the dyadic decomposition of the domain, follows the broad outline of recent works on similar results for genuinely singular (non-truncated) operators in the narrower class of UMD (unconditional martingale differences) spaces, but our setting, the main theorem, and some aspects of its proof, are new. This is based on arXiv:2310.08926.
July6, 2024. 09:30(Beijing time)
Speaker:章志飞(北京大学)
Title: Towards understanding the transition mechanism of laminar flows
Abstract
The hydrodynamics stability has been a main theme in the fluid mechanics since Reynolds's famous experiment in 1883. This field is mainly concerned with the transition of fluid motion from laminar to turbulent flow. On one hand, the eigenvalue analysis showed that the plane Couette flow and pipe Poiseuille flow are linearly stable for any Reynolds number. On the other hand, the experiments showed that these flows could be unstable and transit to turbulence for small but finite perturbations at high Reynolds number. This is so-called Sommerfeld paradoxes. The resolution of these paradoxes is a long-standing problem in the fluid mechanics. In this talk, we introduce some recent progress towards understanding the transition mechanism by two means: pseudospectra and transition threshold problem.
July1, 2024. 15:30(Beijing time)
Speaker:陈华一 (西湖大学)
Title: 平凡度量的算术几何
Abstract
所谓域上的平凡绝对值,是指将域中任何非零元素映为1,将零元映为0 的映射。这样的度量体现的是域的离散拓扑,在数论中往往被排除在研究的兴趣之外。本报告中我将以代数曲线的情形为例介绍与森脇淳的一个工作,展现平凡度量下域上代数簇丰富的算术性质。
June25, 2024. 15:15(Beijing time)
Speaker:Javier Parcet (ICMAT, Madrid)
Title: What do Fourier and Schur idempotents look like?
Abstract
What happens to an $L_p$ function when one truncates its Fourier transform to a domain? This is in the root of foundational problems in harmonic analysis. Fefferman’s ball multiplier theorem (1971) shows that $L_p$-preserving Fourier truncations are associated to domains with flat boundary. What if we truncate on a curved space like a Lie group? And if we truncate the entries of a given matrix? How does it affect its singular numbers? These apparently unrelated problems are interestingly connected. Our talk will be based on a joint work with M. de la Salle and E. Tablate.
June25, 2024. 14:00 (Beijing time)
Speaker: Louis Labuschagne (North-West University)
Title: Quantum Fokker-Planck dynamics
Abstract
The Fokker-Planck equation is a partial differential equation which is a key ingredient in many models in physics. Given that relevant models relate to the description of large systems, quantization of the Fokker-Planck equation should be done in a manner that respects this fact. With this in mind we develop a quantum counterpart of Fokker-Planck dynamics within the context of non-commutative analysis based on general von Neumann algebras. We achieve this by presenting a quantization of the generalized Laplace operator, and by also proposing a potential term conditioned to noncommutative analysis. We next obtain conditions under which the composite term generates Markov dynamics, before in closing examining the asymptotic behaviour of the Markov semigroup thus obtained. We also present a noncommutative Csiszar-Kullback inequality formulated in terms of a notion of relative entropy, and show that for more general systems, good behaviour with respect to this notion of entropy similarly ensures good asymptotic behaviour of the dynamics.
June19, 2024. 15:30 (Beijing time)
Speaker: 朱克和 (SUNY-Albany)
Title: Canonical integral operators on the Fock spaceSingleton mesh patterns in multidimensional permutations
Abstract
In this talk I will present my recent joint work with Professor Xing-Tang Dong of Tianjin University. We introduce and study a two-parameter family of integral operators on the Fock space.We determine exactly when these operators are bounded and when they are unitary. We show that, under the Bargmann transform, these operators include the classical linear canonical transforms as special cases. As an application, we obtain a new unitary projective representation for the special linear group SL(2,R) on the Fock space.
May17, 2024. 10:00 (Beijing time)
Speaker: Sergey Kitaev (University of Strathclyde)
Title: Singleton mesh patterns in multidimensional permutations
Abstract
Permutation patterns is a popular area of research introduced in 1968, but with roots going to the work of Leonhard Euler in 1749.
In this talk, I will present a brand-new notion of a singleton mesh pattern (SMP), which is a multidimensional mesh pattern of length 1. It turns out that avoidance of this pattern in arbitrary large multi-dimensional permutations can be characterised using an invariant of a pattern called its rank. This allows to determine avoidability for an SMP P efficiently, even though determining rank of P is an NP-complete problem. Moreover, using the notion of a minus-antipodal pattern, one can characterise SMPs which occur at most once in any d-dimensional permutation.
I will also discuss several enumerative results regarding the distributions of certain general projective, plus-antipodal, minus-antipodal and hyperplane SMPs.
This is joint work with Sergey Avgustinovich, Jeffrey Liese, Vladimir Potapov and Anna Taranenko.
May16, 2024. 16:00 (Beijing time)
Speaker: Liping Zhu (Renmin University of China)
Title: 非线性相依与独立性检验
Abstract
统计学“始于度量、兴于相关”。度量相关性和检验独立性是统计学领域基本问题,预测和推断是统计学和机器学习领域核心问题。本报告将会回顾统计学领域线性相关和非线性相关各类度量准则,以及独立性检验的最新进展。
May9, 2024. 16:00 (Beijing time)
Speaker: Xiaohua Yao (Central China Normal University)
Title: Some 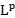 problems from scattering theory
problems from scattering theory
Abstract
In this talk, I will first review some classical results of scattering theory for Schrodinger operator 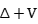 ,including limiting absorption principle, generalized eigenfunction expansions and the existence of wave operators in the context of
,including limiting absorption principle, generalized eigenfunction expansions and the existence of wave operators in the context of 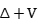 . These concepts/operators also have similar
. These concepts/operators also have similar 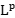 counterparts or
counterparts or 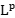 estimates related with harmonic analysis, including uniform Sobolev estimates of resolvent,
estimates related with harmonic analysis, including uniform Sobolev estimates of resolvent, 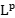 bounds of wave operators and so on. Finally, we also address some related
bounds of wave operators and so on. Finally, we also address some related 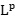 -works associated with higher order Schrodinger operators
-works associated with higher order Schrodinger operators 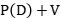 . These are adjoint-works with Haruya Mizutani and Zijun Wan.
. These are adjoint-works with Haruya Mizutani and Zijun Wan.
May6, 2024. 14:30 (Beijing time)
Speaker: Naihuan Jing (North Carolina State University)
Title: Generalized Specht criteria and local unitary equivalence
Abstract
Local unitary equivalence of quantum states is a basic theoretical problem in quantum information. Lots of efforts have been made on finding complete invariants for pure and fixed states. So far only bipartite mixed qubits are known by the Macklin's 18 invariants. We report on some recent progress using hypermatrix algebras and hyperdeterminants on 3-qubits. Joint work with Dobes.May6, 2024. 15:30 (Beijing time)
Speaker: Olivier Mathieu (CNRS, Lyon)
Title: Systoles and Coxeter groups
Abstract
Given a closed hyperbolic surface, a systole is a closed geodesic of shortest length. A generic surface of genus  has a unique systole which cuts it into one or two noncontractible pieces. However, there are closed hyperbolic surfaces of genus
has a unique systole which cuts it into one or two noncontractible pieces. However, there are closed hyperbolic surfaces of genus 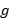 , whose set of systoles fills the surface, i.e. it cuts the surface into polygons. In general, it is easy to find surfaces with a large number of systoles which fill. A classical example is the Bolsa surface of genus 2 with 12 systoles. Here we are interested to find surfaces for which the set of systoles is filling while being small. In fact, our approach provides surfaces with significatively less systoles than the previously known examples. Then we will briefly outline a consequence in Teichmüller theory. Our construction is based on the theory of Coxeter groups, especially the arithmetic properties of the Tits representation. From a geometric viewpoint, it involves hyperbolic tessellations. Although this work mixes hyperbolic geometry and representation theory, our presentation will be quite elementary.
, whose set of systoles fills the surface, i.e. it cuts the surface into polygons. In general, it is easy to find surfaces with a large number of systoles which fill. A classical example is the Bolsa surface of genus 2 with 12 systoles. Here we are interested to find surfaces for which the set of systoles is filling while being small. In fact, our approach provides surfaces with significatively less systoles than the previously known examples. Then we will briefly outline a consequence in Teichmüller theory. Our construction is based on the theory of Coxeter groups, especially the arithmetic properties of the Tits representation. From a geometric viewpoint, it involves hyperbolic tessellations. Although this work mixes hyperbolic geometry and representation theory, our presentation will be quite elementary.
April30, 2024. 16:00 (Beijing time)
Speaker: Shizan Fang (University of Burgundy)
Title: Navier-Stokes equations and geometric interpretation
Abstract
We try to give geometric interpretations on Navier-Stokes equations
April12, 2024. 15:30 (Beijing time)
Speaker: Vicentiu Radulescu(University of Craiova)
Title: Some striking phenomena in the analysis of (p,q)-equations
Abstract
I shall discuss some new recent striking results that appear in the analysis of problems with unbalanced growth. In the isotropic case, I shall point out an interesting discontinuity property of the spectrum. In the second part my talk, I will discuss the anisotropic case and I shall discuss a new case corresponding to equations with mixed regime. Several new research directions will be highlighted in the final part of this talk.
December28, 2023. 16:00 (Beijing time)
Speaker: Meiyue Jiang(Peking University)
Title: Uniqueness of Positive Solutions of Nonlinear Elliptic Equations
Abstract
Let  be a bounded and regular domain. In this talk we will discuss some uniqueness results of positive solutions of the following nonlinear elliptic equation
be a bounded and regular domain. In this talk we will discuss some uniqueness results of positive solutions of the following nonlinear elliptic equation
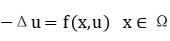
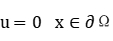
via a kind of convexity of the associated functional
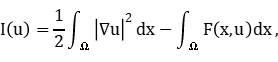
where 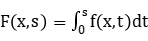 . Some related results for the
. Some related results for the 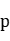 -Laplacian equation and other equations will also be discussed.
-Laplacian equation and other equations will also be discussed.
November24, 2023. 16:00 (Beijing time)
Speaker: Zeqian Chen(Chinese Academy of Sciences)
Title: 量子人工智能的拓扑斯理论形式
Abstract
本报告介绍近期我们用拓扑斯理论(Topos theory)研究人工智能的工作。依据图灵测试对智能给出的科学定义, 我们将人工智能系统定义为由拓扑斯理论所描述的物理系统(Isham等人在2008年建立的物理理论), 它们具有自身的高阶形式语言及逻辑推理系统。特别是,我们用Hilbert空间上算子理论构造相应的拓扑斯以给出量子人工智能系统的数学描述。我们还将介绍量子计算的拓扑斯理论模型。
October27, 2023. 15:00 (Beijing time)
Speaker: Fabcrice Béthuel(Sorbonne Université)
Title: On Sobolev maps between manifolds and branched transportation
Abstract
In the talk, I wish to stress the link between branched transportation theory, and some issues in the study of Sobolev maps between manifold. In particular, I will present a counterexample to the sequential weak density of smooth maps between two manifolds 𝑀 and 𝑁 in the Sobolev space 𝑊1,𝑝 (𝑀, 𝑁), in the case 𝑝 is an integer. It has been shown quite a while ago that, if 𝑝 < 𝑚 = 𝑑𝑖𝑚(𝑀) is not an integer and the [𝑝]-th homotopy group 𝜋[𝑝] (𝑁) of 𝑁 is not trivial, [𝑝] denoting the largest integer less than 𝑝, then smooth maps are not sequentially weakly dense in 𝑊1,𝑝 (𝑀, 𝑁). On the other hand, in the case 𝑝 < 𝑚 is an integer, examples of specific manifolds 𝑀 and 𝑁 have been provided where smooth maps are sequentially weakly dense in 𝑊1,𝑝 (𝑀, 𝑁)with 𝜋[𝑝] (𝑁) ≠ 0, although they are not dense for the strong convergence. This is the case for instance for 𝑀 = 𝐵 𝑚. Such a property does not hold for arbitrary manifolds 𝑁 and integers 𝑝.
The counterexample deals with the case 𝑝=3, 𝑚 ≥ 4 and 𝑁 = 𝑆 2 , for which 𝜋3 (𝑆 2 ) = 𝑍 is related to the Hopf fibration. We provide an explicit map which is not weakly approximable in 𝑊1,3 (𝑀, 𝑆 2 ), by smooth. One of the central ingredients in our argument is related to issues in branched transportation and irrigation theory in the critical exponent case.
October27, 2023. 16:15 (Beijing time)
Speaker: Sami Mustapha (Sorbonne Université)
Title: Potential theory and combinatorics
Abstract
“... But the most general and direct method for resolving questions of probability consists of making them depend on difference equations ...”
The aim of this talk is to illustrate this quote from Laplace (Philosophical essay on probabilities) by developing certain aspects of the theory of discrete potential theory attached to a random walk in 𝑍 𝑑 ; the difference equations playing in this framework the same role played by the PDEs in the theory of the classical potential theory. Although the presentation will be mainly limited to simple walks in quadrants, some extensions to walks in discrete Lipschitzian domains and to inhomogeneous walks will be discussed. The emphasis will be placed on the role that tools from discrete potential theory can play (harmonic functions and discrete caloric functions, maximum principle, Harnack inequalities, boundary Harnack inequalities at the boundary) in establishing optimal estimates for the number of paths confined to a region as well as the number of excursions.
September26, 2023. 14:00 (Beijing time)
Speaker: Adam Skalski (IMPAN)
Title: `What is a good definition? In search of quantum groups'
Abstract
Definitions form a fundamental part of the mathematical study. I will discuss the requirements that mathematicians put on `good' definitions and explain how such definitions develop, based on the notion of a locally compact quantum group, originating in 1970s and 1980s, and reaching a (possibly?) final form in the work of Kustermans and Vaes in 2000. Later developments will also be mentioned, but in general the talk will be accessible to general mathematical audience.
About the speaker: Adam Skalski is a full professor and the scientific director of the Institute of Mathematics of of the Polish Academy of Sciences, and the chairman of ERCOM (European Research Centers on Mathematics). His areas of interest include topological quantum groups, operator algebras and quantum stochastic processes. He has been awarded the Kuratowski Prize of the Polish Mathematical Society in 2008 and the Sierpinski Prize of the Polish Academy of Sciences in 2014. He is one of the executive editors of Studia Mathematica and Banach Center Publications.
June12, 2023. 14:00 (Beijing time)
Speaker: Xiangdong Li(Academy of Methematics and System Science,Chinese Academy of Sciences)
Title: 最优传输问题与经济资源的最优分配
Abstract
1781年,法国数学家G. Monge从军事工程问题中提出了最优传输映射问题。1942年,苏联数学家L. Kantorovich提出了最优传输计划问题,并将其应用于国民经济资源最优分配问题的研究。1975年,Kantorovich与美国数理经济学家T. Koopmans共同分享了Nobel经济学奖。2010年和2018年,法国数学家C. Villani与意大利数学家A. Figalli先后获得菲尔兹奖,其研究工作均与最优传输问题密切有关。在本报告中,我们将回顾最优传输问题的历史发展和重要的标志性成果,并介绍Kantorovich等人关于经济资源最优分配问题的研究成果。
May30, 2023. 16:00 (Beijing time)
Speaker: Jean-Paul Allouche(CNRS, IMJ-PRG)
Title: Playing with Kempner-like harmonic series
Abstract
Though the series of the inverses of integers diverges, a nice,now classical, result of Kempner (in 1914) states that the sum of the inverses of the integers whose expansion in base 10 contains no occurrence of a given digit converges. Several generalizations or extensions of this result have been given. In particular a paper of Farhi (in 2008) proves the somehow unexpected result that
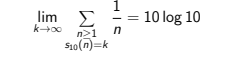
where s10(n) is the sum of the digits of n in base 10.
We show how to extend this result, first by replacing s10(n) with s2(n), the sum of the binary digits of the integer n; then by replacing s2(n) by any binary pattern counting sequence (i.e., any sequence aw(n) that counts the number of occurrences of a fixed block w of 0’s and 1’s in the binary expansion of the integer n).
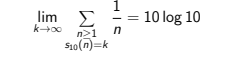
April 11, 2023. 16:00 (Beijing time)
Speaker: Liming Wu(Harbin Institute of Technology,l'Université Clermont-Auvergne)
Title: 马氏过程的集中不等式
Abstract
这个报告的主题是马氏过程观察量的经验均值趋于真实均值的集中不等式,或者说随机算法的错误概率的绝对估计。我将介绍与集中不等式等价的“运费vs Fisher信息量”不等式,以及怎样使用Poincare或logSobolev不等式,与最优传输,熵这些工具去证明“运费vs Fisher信息量”不等式。作为应用例子,我将介绍高维分布Gibbs算法的错误概率绝对估计。
March 7, 2023. 16:00 (Beijing time)
Speaker: Changgui Zhang (University of Lille)
Title: Some problems about a family of linear functional differential equations
Abstract
Given q between 0 and 1, one considers the following problems about the q-difference-differential equation y′(x) = ay(qx) + by(x) + f (x),where a and b are two complex numbers and where f is a rational function:
(1) The pantograph equations following Kato and McLeod;
(2) The indexes of the associated operator d/dx − aσ_q − b;
(3) The connection formulas between zero and infinity;
(4) The asymptotic behavior of the solutions at infinity.
This talk is partially based on a joint work with H. Dai and G. Chen (HITSZ).
November 26, 2022. 10:00 (Beijing time)
Speaker: Yitang Zhang (University of California)
Title: 关于朗道-西格尔零点猜想

